
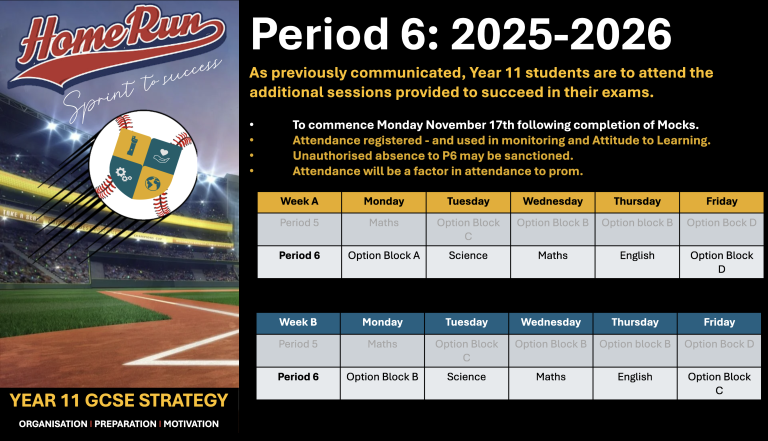
Y11 Period 6 (3pm - 4pm) Revision Sessions (Attendance Compulsory)
Revision Resources
At Newsome Academy, we encourage all students to take a structured and consistent approach to revision and independent study. Effective revision helps students consolidate their learning, build confidence, and achieve their full potential.
To support this, students have access to a range of resources, including subject-specific revision guides, online platforms, and teacher-led materials. Revision guides for each subject can be purchased through ParentPay starting at whole bundles for £30—an 80% discounted rate—ensuring students have everything they need to succeed.

Geography
Natural Hazards: Definition, types, and factors affecting hazard risk.
Tectonic Hazards: Plate margins, earthquakes (causes, effects, responses), volcanoes (risks, advantages, responses).
Weather Hazards: Global atmospheric circulation, tropical storms, UK weather hazards, extreme weather.
Climate Change: Causes (natural and human), evidence, and management strategies.
Ecosystems: Small-scale and global ecosystems.
Tropical Rainforests: Characteristics, deforestation causes and impacts, management strategies.
Hot Deserts: Characteristics, opportunities, challenges, desertification causes, and management.
UK Landscapes: Key locations of upland and lowland areas.
Coastal Landscapes: Erosion, weathering, waves, coastal features, and management strategies.
River Landscapes: Drainage basin features, erosion and transportation processes, formation of waterfalls, meanders, ox-bow lakes, levees, and flooding (causes, impacts, responses).
Urban Issues and Challenges: Urbanisation, megacities, case studies (Rio de Janeiro and Bristol), sustainable urban living (Freiburg), and sustainable traffic management.
Fieldwork: Practice applying knowledge and analysing unfamiliar data, drawing conclusions from fieldwork materials.
Revision Tips:
Use flashcards to memorise key terms and definitions.
Create diagrams for processes like river erosion, tectonic activity, or urban growth.
Practise exam-style questions using case studies to build confidence.
Make a revision timetable, breaking topics into manageable chunks.
Review your revision guides and online resources regularly to reinforce understanding.
History
Germany and the Growth of Democracy (1919–1929): The Weimar Republic, early stages of the Nazi Party.
Hitler’s Rise to Power (1929–1934): The impact of the Great Depression, the Nazi rise, and the establishment of a dictatorship.
Experiences of Germans under the Nazis (1933–1939): Propaganda, Nazis and the Church, opposition to the Nazis, work and home life, young people, and Nazi racial policies.
Origins of the Cold War (1941–1958): The Grand Alliance, the emergence of the two superpowers, mutual suspicion, the Berlin Crisis, the arms race, and divisions in Eastern Europe.
Cold War Crises (1958–1970): The Berlin Question, construction of the Berlin Wall, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and the Prague Spring.
End of the Cold War (1970–1991): Detente, Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, the Second Cold War, Gorbachev’s “New Thinking,” Eastern Europe’s move away from Soviet control, and the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Revision Tips:
Create timelines to visualise events and causes/consequences.
Use flashcards for key dates, people, and events.
Write short paragraph answers to practise explaining causes, consequences, and significance.
Focus on case studies for Germany (Weimar, Hitler) and the Cold War crises.
Regularly review notes and past papers to build confidence and speed.
RE
Religion and Life: Origins of the Universe, the environment and stewardship, animal rights, abortion, euthanasia, and the afterlife.
Religion, Peace and Conflict: Peace and conflict, weapons of mass destruction, and peacemaking.
Religion, Crime and Punishment: Religion and the law, crime, forgiveness, punishment, and the death penalty.
Religion, Relationships and Families: Sexuality and sexual relationships, contraception, marriage, divorce, families, and gender equality.
Beliefs, Teachings and Practices: The Trinity, creation, evil and suffering, the afterlife, Jesus and salvation.
Worship and Practice: Different forms of worship, the sacraments, prayer and pilgrimage, Christmas and Easter, and the work of the Church.
Revision Tips:
Make flashcards for key teachings, religious beliefs, and important quotes.
Use diagrams or mind maps to link concepts and themes.
Practice evaluating and explaining different viewpoints for exam-style questions.
Review case studies and examples to support your answers.
Regularly test yourself using past papers or online quizzes to build confidence.
Business
To succeed in NCFE Business, it’s important to understand key concepts, apply knowledge to practical scenarios and practise assessment tasks. Revision should focus on both theory and real-world application to build confidence and achieve your best.
Key areas to focus on include:
Enterprise and Entrepreneurs: Characteristics of entrepreneurs, business opportunities, and spotting market needs.
Marketing and Market Research: Methods of market research, understanding customer needs, and using the marketing mix (product, price, place, promotion).
Business Operations: Types of business activity, production methods, quality, and supply chains.
Finance: Revenue, costs, profit, cash flow, and understanding different sources of finance.
Human Resources: Recruitment, training, motivation, and organisational structures.
Business Environment: The impact of economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors on business decisions.
Revision Tips:
Make flashcards for key terms, definitions, and processes.
Use diagrams and flowcharts to visualise business concepts like production methods or marketing processes.
Practise applied assessment tasks using case studies and real-life examples.
Review past NCFE exam materials to familiarise yourself with question styles and expectations.
Mr Hart Business is a great revision site!
English
Language
Paper 1: Explorations in Creative Reading and Writing (Language)
Reading Skills:
Understand explicit and implicit meanings in texts
Analyse language, structure and form to explain how writers create effects
Use quotations effectively to support points
Compare texts (if applicable) and identify similarities/differences
Writing Skills:
Produce clear, coherent writing for a specified audience and purpose
Use a range of sentence structures and vocabulary to create effects
Organise ideas logically with paragraphs
Apply tone, register and stylistic techniques appropriately
Revision Tips:
Annotate extracts, highlighting literary techniques (e.g., imagery, metaphor, repetition)
Practise timed writing tasks to improve pacing
Plan answers before writing to ensure structured responses
Paper 2: Writers’ Viewpoints and Perspectives
Reading Skills:
Analyse how writers present ideas, themes, and perspectives
Evaluate effectiveness of language and structure
Compare two texts critically, identifying similarities and differences in viewpoints
Use evidence and quotations to justify answers
Writing Skills:
Write a persuasive or discursive piece for a specific audience
Present a clear viewpoint, using evidence and examples to support ideas
Apply formal or appropriate tone depending on task
Structure writing logically with cohesion and clarity
Revision Tips:
Practise comparing texts for language, structure, and purpose
Summarise main ideas before writing to clarify viewpoint
Use PEE (Point, Evidence, Explanation) or PETE (Point, Evidence, Technique, Effect) for structured responses
Literature
Key Skills:
Analyse characters, themes, and settings
Explore writers’ methods and intentions
Use quotations effectively in analysis
Contextual knowledge: Historical, cultural, and social context of texts
Set Texts (Examples, confirm with your class):
Macbeth – key quotes, characters, themes, dramatic devices
A Christmas Carol – characterisation, narrative structure, themes
An Inspector Calls – social context, character motivations, themes
Poetry Anthology – key poems, themes, techniques, comparisons
Revision Tips:
Make character/theme tables for each text
Create quotations banks with techniques annotated
Practise exam-style questions and time yourself
Use past papers and mark schemes to understand exam expectations
Some Useful Links:
Health and Fitness
To succeed in NCFE Health and Fitness, it’s important to understand key concepts, apply knowledge to scenarios and practise assessment tasks. Focus your revision on theory, practical application and understanding how fitness and health interrelate.
Key Topics to Revise
1. Health and Wellbeing
Definitions of health: Physical, social, and mental wellbeing
Factors affecting health and wellbeing: Lifestyle, diet, exercise and environment
Short-term and long-term impacts of exercise on the body and mind
2. Fitness and Components of Fitness
Components of fitness: Cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, body composition and agility
How to measure and improve each component
Benefits of regular exercise on physical and mental health
3. Principles of Training and Exercise
Principles: Specificity, progression, overload, reversibility and individuality
Methods of training: Continuous, interval, circuit, weight/resistance and flexibility training
Planning and adapting fitness programs safely
4. Lifestyle and Physical Activity
Importance of regular physical activity across all ages
Barriers to participation and strategies to overcome them
Role of diet, hydration and rest in supporting fitness
5. Monitoring and Assessing Fitness
How to assess health and fitness levels
Recording and interpreting data to set targets
Adapting training plans based on results
6. Safety and Injury Prevention
Importance of warm-ups and cool-downs
Common injuries in fitness and prevention strategies
Safe use of equipment and facilities
Revision Tips:
Use flashcards for key terms, components, and principles
Create diagrams or tables linking fitness components, methods, and benefits
Practise applied questions and scenarios to show understanding
Review case studies from practical sessions or past assessments
Make a revision timetable and cover theory alongside practical application
Here is a Revision list to help you.
Food and Cookery
To do well in NCFE Food and Cookery, it’s important to understand the theory, practical skills and the link between nutrition and health. Focus your revision on the following key areas:
. How Food Can Cause Ill Health
Understand the relationship between diet and diseases (e.g., obesity, diabetes, heart disease)
Recognise the effects of poor food hygiene and contamination
2. Dietary Needs
Requirements for different age groups, lifestyles, and health conditions
Special dietary considerations (allergies, intolerances, vegetarian/vegan diets)
3. Diet and Good Health
Principles of a balanced diet
How diet supports physical and mental wellbeing
Effects of overconsumption or deficiency
4. Macronutrients
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats: sources, functions, and effects on the body
Energy content and role in growth, repair, and activity
5. Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals: key sources, functions, and deficiency/excess effects
How micronutrients contribute to overall health
6. Functions
The role of nutrients in the body: energy, growth, repair, regulation, and protection
Understanding water, fibre, and their importance in the diet
7. Heat Transfer
Methods of heat transfer in cooking: conduction, convection, radiation
How different cooking methods affect nutrients, texture, and safety
Take a look at the links below for more topic based revision materials:
Revision Tips:
Use diagrams and charts to visualise nutrients, functions, and sources
Create flashcards for key definitions, examples, and cooking techniques
Practise applied questions, linking nutrition theory to practical cooking
Review practical tasks and case studies to reinforce learning
MFL
To succeed in French and German, it’s important to practice vocabulary, grammar, sentence structures and all four language skills (reading, writing, speaking and listening). Regular revision will help you build confidence and fluency.
Key Revision Resources:
Vocabulary Lists: Essential words and phrases for all topics studied in class
Sentence Builders: Ready-made structures to help form accurate sentences and paragraphs
Class-Specific Resources: Additional exercises, quizzes, and guidance are available on Microsoft Teams
- Key Links are:
- French vocabulary list
- Sentence builders
Revision Tips:
Use flashcards to learn and test vocabulary for both languages daily
Practise writing sentences and short paragraphs using sentence builders
Test yourself on verbs, tenses, and common expressions
Listen to spoken French and German and practise speaking aloud to improve pronunciation and fluency
Use Teams regularly to access worksheets, quizzes, and teacher feedback
Maths
To succeed in Maths, it’s important to know key topics, practise problem-solving, and develop exam strategies. Focus on understanding concepts, memorising formulae, and applying methods to different types of questions.
AQA Higher Content
Number: Fractions, decimals, percentages, powers, roots, standard form, bounds, ratios, and proportion
Algebra: Expressions, formulae, equations, inequalities, sequences, graphs, factorising, expanding, and simultaneous equations
Geometry & Measures: Angles, constructions, transformations, area, volume, Pythagoras’ theorem, trigonometry, circles, loci, and vectors
Probability & Statistics: Probability rules, combined events, sampling, averages, range, and interpreting charts/graphs
Ratio & Proportion: Direct and inverse proportion, compound measures, and problem-solving
OCR Foundation Content
Number: Basic calculations, fractions, decimals, percentages, ratio, and proportion
Algebra: Simple equations, sequences, expressions, graphs, and inequalities
Geometry & Measures: Angles, perimeter, area, volume, symmetry, basic trigonometry, and transformations
Probability & Statistics: Basic probability, averages, interpreting data, charts, and tables
Problem-Solving: Applying knowledge to word problems and real-life scenarios
Revision Tips:
Use past papers and mark schemes to practise exam-style questions
Create formula sheets and key facts for quick reference
Practise timed questions to improve speed and accuracy
Break topics into manageable chunks and revise regularly
Work on weak areas first and seek help from teachers or online resources
Science
Effective revision for Science requires understanding key concepts, practising calculations and applying knowledge to exam-style questions. Focus on using diagrams, notes and past papers to consolidate learning.
Click on the links below for a detailed breakdown and revision checklist of all Science papers and their contents.
AQA Combined Science (Trilogy) – Foundation (F) – Groups: 11M, 11N, 11O, 11W
AQA Combined Science (Trilogy) – Higher (H) – 11E
AQA Separate Sciences (Triple)
Paper 1
Paper 2
Revision Tips:
Use diagrams, flashcards, and mind maps for key concepts
Practise calculations and exam questions for Chemistry and Physics
Review required practicals and experiment data
Break revision into small, focused topics to avoid overload
Use past papers and mark schemes to practise timing and exam technique